Stainless steel tubing (or SS tubing for short) is a popular metal form used in a broad range of industries. As hollow, cylindrical forms, stainless steel tubing or pipes work perfectly as both stand-alone channels through which fluids (gases and liquids) can pass and as parts of larger equipment or systems. Read More…
Cada Stainless & Alloys has the stainless steel tubing that you need. We also specialize in the supply of stainless steel strips and coils, providing many finishing options, processing options, and other customization options.

As stainless steel producers, Source 21 specializes in hard-to-find materials. We produce all tempers plus commercial and exotic stainless steel. You choose from our inventory or we can custom produce to your needs. An ISO 9001:2000 registered company; we maintain comprehensive inventories at our various US processing locations to facilitate quick shipments. Check out our website!

All Metal Sales is a leading-supplier of stainless steel tubing, stainless steel pipe, thin wall tubing, precision tubing and small diameter tubing. We focus on superior customer service, premium quality and quick turnaround times in order to best meet your needs.

More Stainless Steel Tubing Manufacturers
Stainless steel tubing, fabricated from high-chromium, corrosion-resistant alloys, plays a pivotal role in a diverse range of industries due to its unmatched mechanical properties, longevity, and ability to withstand harsh environments. Understanding the production, applications, and benefits of stainless steel tubing is essential for professionals and buyers seeking reliable solutions for fluid transport, structural frameworks, and precision components.
The manufacturing process of stainless steel tubing begins with stainless steel billets or strips. These raw materials are heated and shaped into cylindrical forms, then processed through methods such as hot or cold rolling, welding, or seamless extrusion. Each fabrication technique is chosen based on the desired tube specifications, tolerances, and intended end-use. The result is a robust product that can be customized in size, thickness, and grade, ensuring an exact fit for specific applications.
Stainless steel tubing is available in a wide array of sizes, wall thicknesses, and grades tailored to diverse industry requirements. Tubing dimensions are typically defined by outside diameter (OD), inside diameter (ID), and wall thickness. Shape options include round, square, and rectangular tubing, with round tubing being the most prevalent due to its efficiency in fluid transport and pressure containment.
When evaluating stainless steel piping versus stainless steel tubing, it is important to recognize both their similarities and differences. While both are made from stainless steel alloys and offer corrosion resistance and durability, their primary distinctions lie in size, standards, joining methods, and applications. Stainless steel piping, with larger diameters and thicker walls, is designed primarily for the high-pressure transport of liquids or gases. This makes it indispensable in sectors such as oil and gas, petrochemical processing, chemical manufacturing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and plumbing infrastructure. Piping systems are engineered to meet rigorous standards—such as ASME B31.3 and API 5L—and are typically joined using welded connections to ensure leak-free, high-pressure operation.
In contrast, stainless steel tubing features smaller dimensions and thinner walls and is used for more precise applications, including instrumentation lines, heat exchangers, hydraulic systems, and architectural elements. Tubing is often manufactured to standards such as ASTM A269 or ASTM A554, and can be joined using welding, compression fittings, or mechanical connectors, providing flexibility in installation and maintenance. Tubing’s smaller scale and customizable nature also make it a popular choice for laboratory, medical, and decorative purposes, where appearance and precision are paramount.
Both stainless steel piping and tubing benefit from the inherent corrosion resistance, strength, and long service life of their material. The choice between piping and tubing ultimately depends on the application’s volume, pressure, and regulatory requirements.
History of Stainless Steel Tubing
The evolution of steel tubing is intertwined with the advancement of civilization and technology. Early societies—including the Egyptians, Chinese, and Greeks—engineered primitive piping systems from copper, bamboo, clay, stone, and bronze for water transport. The Romans and Persians built sophisticated aqueducts, while in first-century Europe, lead pipes became common. Colonial Boston’s 1652 waterworks utilized hollowed logs for piping, and redwood trees in the American West later provided resistance to corrosion and fungi.
The Industrial Revolution marked a turning point, as engineer William Murdock repurposed musket barrels into a coal lamp system, highlighting the need for durable metal tubing. The introduction of the Bessemer process in the mid-19th century revolutionized iron and steel production, enabling mass manufacture of tubes and pipes. Early welded tubes were susceptible to failure under pressure, but by 1840, seamless tubes were produced by drilling and drawing billets—a process refined in 1888 by casting billets around fireproof cores.
The invention of stainless steel in 1912 by Harry Brearley transformed the industry, providing a material with exceptional corrosion resistance, mechanical robustness, and versatility. Today, stainless steel tubing and stainless steel piping are foundational to structural, industrial, and transportation systems in modern society, supporting everything from infrastructure and energy to aerospace and medical devices.
Materials of Stainless Steel Tubing
Selecting the optimal stainless steel grade for tubing or piping is a complex process that must account for the application’s operating conditions, corrosion risks, mechanical demands, and compliance with industry standards. The most commonly specified stainless steel grades for tubing and piping include:
- Austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 304/304L, 316/316L): These are prized for their outstanding corrosion resistance, excellent mechanical strength, and ductility. Austenitic grades are the mainstay in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and plumbing. Their versatility makes them suitable for both piping and tubing, including sterile environments where contamination must be avoided.
- Duplex stainless steels (e.g., 2205, 2507): Featuring a microstructure that blends austenite and ferrite phases, duplex grades deliver higher strength and superior resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking. They are ideal for demanding applications such as offshore oil and gas, desalination plants, and chemical processing where aggressive corrosion is a concern.
- Ferritic stainless steels (e.g., 430): Known for their resistance to stress corrosion cracking and high-temperature scaling, ferritic steels are employed in automotive exhaust systems, industrial furnaces, and certain architectural elements. While their corrosion resistance is less than austenitic or duplex grades, they offer high heat tolerance and formability.
- Martensitic stainless steels (e.g., 410): These alloys offer high strength, hardness, and wear resistance, with moderate corrosion resistance. Martensitic stainless steels are often found in pump shafts, valve components, cutlery, and select piping systems where mechanical durability is essential.
How do you choose the right stainless steel grade for your application? Consider the type of fluid or gas being transported, operating temperature and pressure, exposure to chemicals or saltwater, and the need for sanitary or aesthetic finishes. Consulting engineering specifications, industry standards (such as ASTM, ASME, or ISO), and materials engineers is crucial for ensuring safety, compliance, and optimal performance.
Some stainless steel grades are preferred for specific uses:
- Stainless Steels Commonly Used for Piping:
- 304/304L (UNS S30400/S30403): This austenitic alloy is widely used in general-purpose piping for its weldability, corrosion resistance, and strength. It excels in chemical plants, food and beverage facilities, and general manufacturing.
- 321 (UNS S32100): Stabilized with titanium, this grade resists intergranular corrosion at high temperatures. It is commonly specified for heat exchangers, furnace components, and high-temperature piping systems.
- Stainless Steels Commonly Used for Tubing:
- 304/304L: This grade’s versatility and resistance to corrosion make it a mainstay for instrument lines, heat exchangers, and architectural tubing.
- 316/316L (UNS S31600/S31603): With enhanced molybdenum content, 316/316L provides superior corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-rich environments. It is preferred for chemical processing, marine, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage applications.
- 409 (UNS S40900): A ferritic grade primarily used in automotive exhaust systems, offering high-temperature scaling resistance and cost-effectiveness.
Not sure which stainless steel tubing grade is right for your project? Evaluate your application’s unique requirements, including pressure and temperature demands, exposure to corrosive agents, and regulatory standards. Consulting with a reputable manufacturer or materials engineer can help ensure the safest and most cost-effective selection.
Stainless Steel Tubing Production
Stainless steel tubing and piping are produced as either welded or seamless products. The choice depends on the application’s pressure requirements, mechanical stress, and budget considerations.
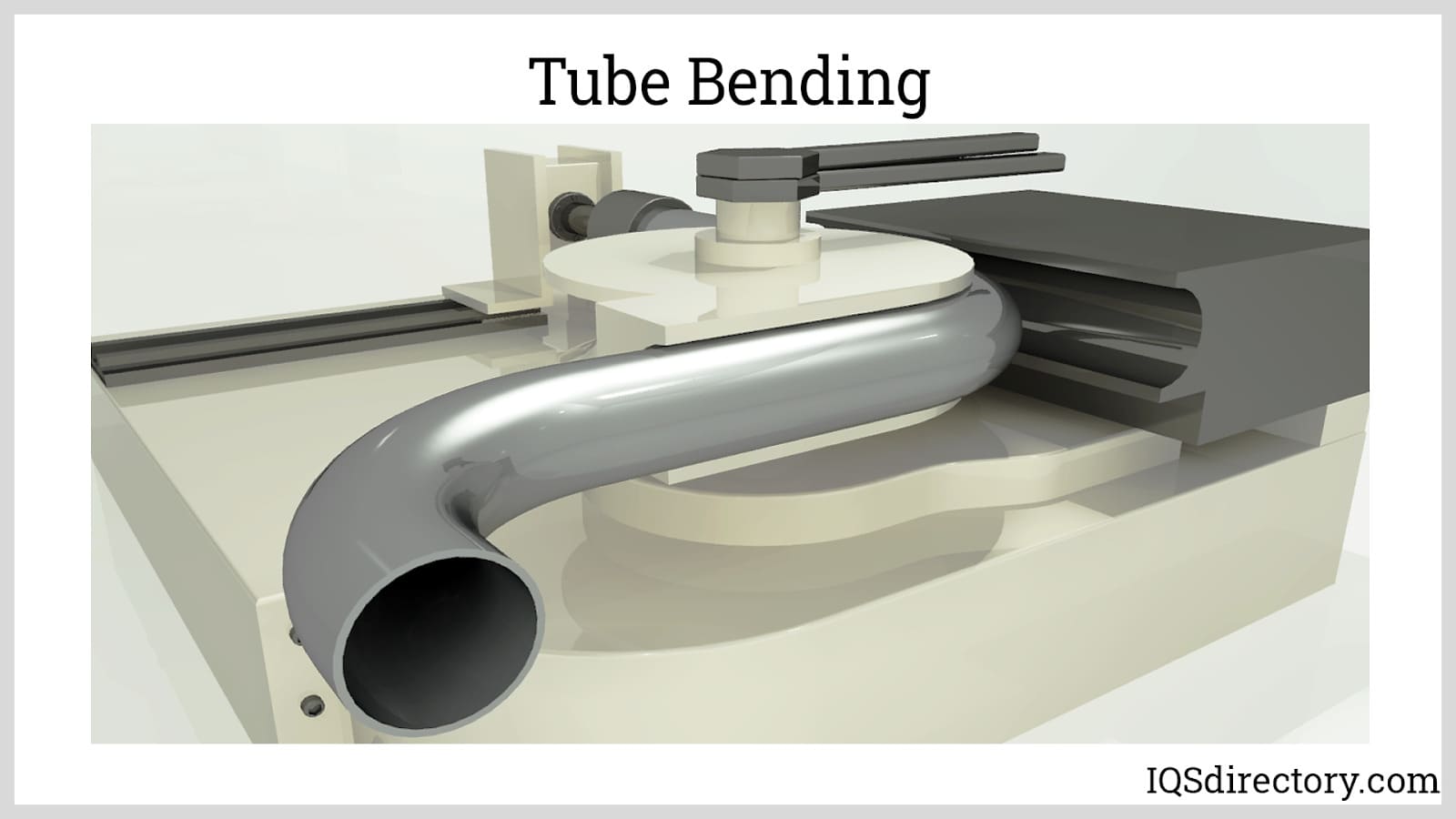
- Welded tubing: Manufactured by rolling stainless steel strips or coils into a round shape, then fusing the edges using electric resistance welding (ERW) or laser welding. After weld formation, the seam is cleaned and the tube is resized to precise specifications. ERW tubing offers cost savings and is widely used for structural, decorative, and lower-pressure fluid transport applications.
- Seamless tubing: Produced by piercing a solid billet and drawing it over a mandrel to create a hollow tube. This method eliminates seams, resulting in tubing with superior strength and resistance to splitting under high pressure. Seamless tubing is favored for critical pressure applications, such as hydraulic lines, high-performance heat exchangers, and instrumentation systems.
Additional forming techniques include metal turning or spin forming, where sheet metal discs are shaped on a CNC lathe to create concentric tubes, and specialized reduction mills that finalize tube dimensions and surface finishes. Technological advancements in precision forming and metallurgical control have enabled manufacturers to produce tubing with tight tolerances, consistent wall thickness, and superior surface quality.
Customizing Stainless Steel Tubing
The adaptability of stainless steel tubing is evident in its wide range of sizes, shapes, and finishes, serving everything from large-scale industrial systems to micro-scale medical devices.
- Size and Gauge: Pipes are typically larger, serving bulk fluid transport, while tubes can be manufactured in extremely small sizes—such as hypodermic tubing for needles and catheters, with internal diameters as small as 0.002 inches. Each size is defined by its internal and external diameters and assigned a specific gauge.
- Types of Tubing:
- Welded tubing (ERW): Cost-effective, suitable for structural and decorative uses.
- Seamless tubing: Ideal for high-pressure, critical applications.
- Square and rectangular tubing: Used in frameworks, handrails, and architectural elements for their strength and aesthetic.
- Corrugated tubing: Flexible, PVC-coated options provide vibration dampening and adaptability in confined spaces.
- Pipe Fittings: Essential accessories for any tubing or piping system, including elbows, tees, reducers, threaded nipples, plugs, and caps. Proper selection and sealing of fittings are crucial for leak prevention and system integrity.
What are the most common customizations requested for stainless steel tubing? Buyers often specify custom lengths, wall thicknesses, surface finishes (polished, satin, mirror), and special coatings for enhanced chemical or abrasion resistance. For sanitary or food-grade tubing, electropolished interiors are preferred.
Types of Stainless Steel Tubing
The broad utility of stainless steel tubing is reflected in the variety of types available to match unique application needs.
- Round tubing: Standard for most fluid transport, heat exchangers, and structural applications.
- Square and rectangular tubing: Favored in construction for railings, frames, and supports.
- Hypodermic tubing: Ultra-fine, precision tubing for medical, laboratory, and instrumentation use.
- Corrugated tubing: Flexible and vibration-resistant, used in gas lines, HVAC, and industrial machinery.
Looking for specialized stainless steel tubing solutions? Consider your application’s structural, sanitary, and environmental demands to determine the best type and configuration.
Applications of Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless steel tubing is indispensable in a vast range of industries, owing to its unique blend of strength, corrosion resistance, and adaptability. Key application sectors include:
- Industrial and Process Applications: Used for transporting fluids and gases in chemical plants, oil and gas refineries, and power generation facilities. Its resilience to chemicals and high temperatures is critical for safety and efficiency.
- Heat Transfer Systems: Central to the function of heat exchangers, condensers, and boilers due to its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Automotive Industry: Essential for exhaust systems, fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and structural supports. Stainless steel tubing withstands vibration, temperature extremes, and corrosive exhaust gases.
- Architecture and Construction: Favored for handrails, balustrades, structural supports, and decorative elements. Its aesthetic appeal, strength, and low maintenance make it a popular choice in both commercial and residential projects.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Stainless steel’s biocompatibility makes it ideal for surgical instruments, implantable devices, catheters, and laboratory equipment. Its smooth, non-porous surface supports sterilization and hygiene.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Used in sanitary piping, transfer lines, and processing equipment where hygiene and resistance to aggressive cleaning agents are required.
- Aerospace and Defense: Precision tubing is used for hydraulic lines, engine components, and structural assemblies where weight, strength, and reliability are paramount.
- Emerging Technologies: Increasingly utilized in renewable energy, hydrogen transport, and advanced water treatment systems, where reliability, purity, and sustainability are crucial.
How is stainless steel tubing used in your industry? Understanding your sector’s unique needs—such as pressure, hygiene, weight, or corrosion resistance—can help identify the best tubing solution.
Considerations of Stainless Steel Tubing
When specifying or purchasing stainless steel tubing, several considerations come into play:
- Cost: Stainless steel tubing is more expensive than carbon steel or plastic alternatives, due to complex alloying, precision production, and higher raw material costs. Specialty grades and tighter tolerances increase price.
- Lead Time: Custom sizes, finishes, or specialty grades may require longer production times.
- Environmental Impact: The production is energy-intensive and may generate waste or emissions, but many manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices to minimize environmental footprint.
- Maintenance: Stainless steel tubing requires periodic cleaning to maintain appearance and corrosion resistance, especially in high-purity or sanitary environments.
- Material Selection: Choosing the correct grade is crucial to avoid premature failure or compatibility issues.
What factors should you evaluate when selecting stainless steel tubing? Review your application’s chemical exposure, mechanical demands, regulatory standards, installation environment, and maintenance expectations.
Stainless Steel Tubing Manufacturing
Stainless steel tubing manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation, employing advanced metallurgical processes and state-of-the-art manufacturing technologies to deliver high-quality products. Key focus areas include:
- Process Optimization: Streamlining production to reduce material waste, energy consumption, and costs without compromising quality. Techniques such as lean manufacturing, automated quality checks, and precision forming help maintain consistency and efficiency.
- Alloy Development: Ongoing research and development of new stainless steel formulations offer improved corrosion resistance, weldability, and mechanical properties tailored for specific industries.
- Sustainability: Adoption of renewable energy, advanced recycling systems, and eco-friendly surface treatments reduce environmental impact and support circular economy principles.
- Technical Support and Customization: Close collaboration with engineers, architects, and end users ensures tubing solutions are precisely matched to project requirements, from material selection to design and finishing.
- Surface Treatments and Finishes: Advanced coatings, electropolishing, passivation, and mechanical polishing enhance both durability and ease of maintenance, supporting sanitary and aesthetic applications.
Considering a custom stainless steel tubing project? Work with manufacturers who provide comprehensive technical support, extensive customization capabilities, and a proven track record of quality assurance.
Benefits of Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless steel tubing offers a compelling array of benefits that drive its popularity across so many industries and applications:
- Corrosion Resistance: Withstands exposure to moisture, chemicals, and harsh environments, minimizing rust and degradation over time.
- Strength and Durability: Maintains structural integrity under high pressure, mechanical load, and temperature extremes.
- Hygiene and Cleanability: Non-porous, smooth surfaces are easy to sanitize, making stainless steel tubing ideal for medical, food, and pharmaceutical use.
- Versatility: Available in multiple shapes, sizes, and grades, supporting everything from architectural trim to high-performance fuel lines.
- Recyclability and Sustainability: Stainless steel is 100% recyclable, supporting green building standards and reducing environmental impact.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Offers a sleek, modern appearance for visible architectural and design elements.
Why should you choose stainless steel tubing for your next project? Consider its long-term value, reduced maintenance requirements, aesthetic versatility, and ability to meet stringent regulatory and performance standards.
Stainless Steel’s Potential Future
The future of stainless steel tubing is bright, fueled by ongoing advancements in alloy chemistry, manufacturing automation, and sustainability. Manufacturers are developing new grades with enhanced corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and temperature tolerance, opening doors to new applications in renewable energy, hydrogen infrastructure, electric vehicles, and advanced water treatment.
Digitalization and automation are transforming production, yielding more precise, consistent, and cost-effective products. The push for environmental responsibility is accelerating the adoption of renewable energy, recycling, and clean production techniques within the stainless steel tubing industry.
Which industries will drive future demand for stainless steel tubing? Look to renewable energy, transportation, infrastructure, and high-tech sectors, all of which require reliable, high-performance, and sustainable materials.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Tubing Manufacturer
For the best results when purchasing stainless steel tubing, compare various manufacturers using our directory. Each manufacturer has a detailed business profile showcasing their expertise and capabilities, along with a contact form for inquiries or quotes. Use our patented website previewer to quickly understand each company’s specialties. Then, utilize our streamlined RFQ form to contact multiple manufacturers efficiently.
How do you evaluate and select the best stainless steel tubing supplier? Prioritize manufacturers with demonstrated experience in your target industry, comprehensive quality control systems, advanced customization capabilities, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
Ready to find the perfect stainless steel tubing solution? Explore our directory, review supplier profiles, and submit your requirements today to connect with industry-leading manufacturers who can deliver high-quality, cost-effective tubing tailored to your unique application.
What is stainless steel tubing and how is it made?
Stainless steel tubing is a cylindrical product fabricated from high-chromium, corrosion-resistant alloys. It is made by shaping stainless steel billets or strips through processes such as hot or cold rolling, welding, or seamless extrusion. The chosen manufacturing method depends on the required tube specifications, and the tubes can be customized in size, thickness, and grade to match specific applications.
What is the difference between stainless steel piping and tubing?
Stainless steel piping generally has larger diameters and thicker walls, making it suitable for high-pressure transport of liquids or gases, whereas tubing features smaller dimensions and thinner walls for more precise applications. Piping and tubing differ in standards, joining methods, and industry usage, with piping installed in systems like oil and gas, and tubing used for instrumentation lines, medical devices, and architectural elements.
How do you choose the right stainless steel grade for tubing?
Choosing the correct stainless steel grade depends on operating temperature, pressure, corrosion risks, sanitation needs, and compliance with industry standards. Austenitic grades like 304/304L and 316/316L are popular for their corrosion resistance, while duplex, ferritic, and martensitic grades are selected for their specialized properties. Consulting engineering specifications and industry standards is crucial for making the right selection.
What types of stainless steel tubing are available?
Stainless steel tubing comes in various types including round, square, and rectangular tubing, as well as specialty varieties like hypodermic and corrugated tubing. Each type is engineered for specific applications—round tubing is common for fluid transport, while square and rectangular tubing are favored in construction and architecture. Hypodermic tubing is used in medical and lab settings for its precision.
What are the main applications for stainless steel tubing?
Stainless steel tubing is widely used in industrial processing, heat transfer systems, automotive manufacturing, architecture, medical and pharmaceutical equipment, food and beverage processing, aerospace, and emerging technologies. Its strength, corrosion resistance, and ease of sanitation make it suitable for demanding and sanitary environments alike.
What are the benefits of using stainless steel tubing?
Stainless steel tubing offers corrosion resistance, strength, durability, hygiene, versatility in shapes and sizes, recyclability, and aesthetic appeal. These attributes make it a preferred choice in industries that demand reliability, longevity, easy maintenance, and regulatory compliance.
What factors should you consider when buying stainless steel tubing?
Key considerations include application-specific chemical exposure, pressure and temperature requirements, compliance with standards, cost, lead time for customizations, environmental impact, and the required material grade. Proper maintenance and compatibility with fittings are also important for safe and effective use.
How can you select the best stainless steel tubing manufacturer?
Evaluate manufacturers based on their experience in your industry, quality control processes, ability to customize products, technical support, and commitment to sustainable practices. Reviewing business profiles and communicating requirements through supplier directories can help you find the most suitable partner for your project.




 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers Aluminum
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Magnets
Magnets Nickel
Nickel Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services